Spring 解析 Controller 注解全过程
Spring 解析 Controller 注解全过程
参考
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 代码解释说明
前言
为了方便研究 Spring 内存马,需要提前对 Spring Web 的框架进行分析研究。
用例
首先写一个用于调试测试的 Controller,如下。这样我们直接访问路由 /test 即可看到一个回显的字符串在 HTML 上。
package com.example.springshell;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import java.io.IOException;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@GetMapping
public void Test(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// System.out.println("test");
response.getWriter().println("test");
}
}
问题 1:
@Controller是什么?为什么选择 Controller?是否有其他类似注解?1.1
@Controller是什么? Spring MVC 提供了基于注释的编程模型,其中@Controller和@RestController组件使用注释来表达请求映射、请求输入、异常处理等。带注释的控制器具有灵活的方法签名,并且不必扩展基类或实现特定的接口。1.2 为什么选择 Controller? 因为目前常见的 Webshell 是 Controller Webshell。
1.3 是否有其他类似注解? 还有
@Controller、@Service和@Repository等等。
时序图
待补充
我们这里的分析分为两个阶段,在
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh 我们注释了两个主要的代码,我们接下来分为两个部分进行分析。一个是扫描 class 并且注册 为bean,第二个是解析 Controller 和 GetMapping 注解。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // 1.扫描 class 并且转换成 bean
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // 2.解析 Controller 和 GetMapping 注解
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
...
}
}
在 refresh 方法中,ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); 准备了后面需要的 bean 工厂类。
来到我们需要步入的方法,finishBeanFactoryInitialization 方法, 这个方法会实例化所有剩余的(非惰性初始化)单例。
(non-lazy-init) singletons (非惰性初始化单例)是什么?
延迟初始化的 bean 告诉 IoC 容器在第一次请求时而不是在启动时创建一个 bean 实例。也就是说 lazy-init 单例在这里不被加载。
doScan 扫描 bean
我们将断点打在 org.springframework.context.annotation.ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#doScan,可以得到以下调用链。
doScan:294, ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner (org.springframework.context.annotation)
parse:128, ComponentScanAnnotationParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
doProcessConfigurationClass:289, ConfigurationClassParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
processConfigurationClass:243, ConfigurationClassParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
parse:196, ConfigurationClassParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
parse:164, ConfigurationClassParser (org.springframework.context.annotation)
processConfigBeanDefinitions:415, ConfigurationClassPostProcessor (org.springframework.context.annotation)
postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry:287, ConfigurationClassPostProcessor (org.springframework.context.annotation)
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors:344, PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate (org.springframework.context.support)
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors:115, PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate (org.springframework.context.support)
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors:779, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)
refresh:597, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)
refresh:146, ServletWebServerApplicationContext (org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context)
refresh:738, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)
refreshContext:440, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)
run:316, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)
run:1306, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)
run:1295, SpringApplication (org.springframework.boot)
main:10, SpringMemshellApplication (ikun.researching.springmemshell)
我们可以参考 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 代码解释说明 ,看看 Spring 是如何从 .class 解析成一个 bean 的。我们一直步入到 org.springframework.context.annotation.ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#doScan
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) { // 扫描 com.example.springshell (classpath) 下的 class
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage); // 查找符合条件的候选组件
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition abstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition(abstractBeanDefinition, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition annotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(annotatedBeanDefinition); // 处理几个注解:Lazy,Primary,DependsOn,Role,Description
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder =
AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry); // 注册 Bean 定义
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
查找符合条件的候选组件的时候,获取到 class 里面的元数据(metadata),里面包含了 class 里面含有哪些注解。包含以下注解的 class 返回是候选组件,后续就会加入 BeanDefinition 集合里面去,后续进入 for 循环处理。
接着,registerBeanDefinition 方法负责将 bean 的元信息(包括类名、属性、作用域等信息)注册到 Spring 的 BeanFactory 中。一旦 bean 的元信息被注册到 BeanFactory 中,容器就具备了创建、配置和管理 bean 的能力。
解析 Controller 和 GetMapping 注解
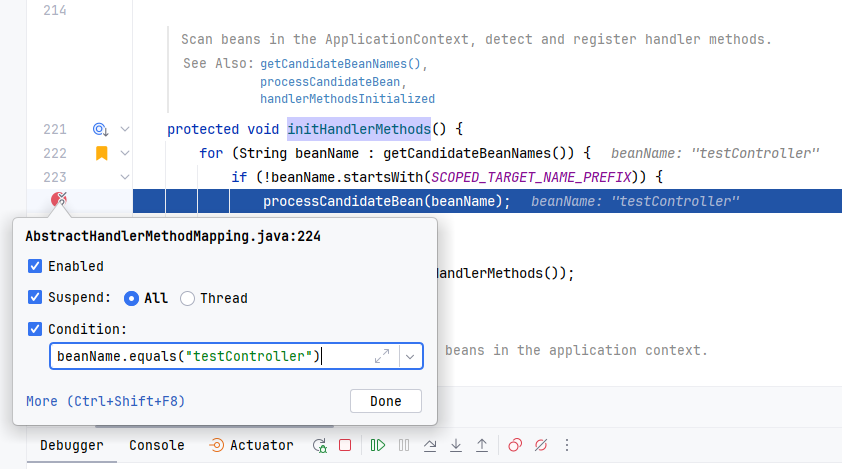
我们将断点打在 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#initHandlerMethods
这里将会扫描 ApplicationContext 中的 bean,检测并注册处理程序方法。
所以这里循环会拿到其他不是我们测试的 bean,我们想要的 bean 是
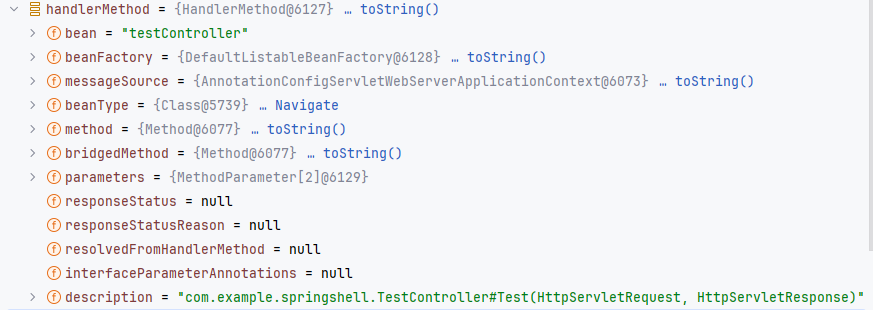
TestController。为此,我们为我们的断点添加一个条件,beanName.equals("testController")。这样就可直接在获取到目标 bean 之后在断点停下,例如上图。可以看到我们拿到的
beanName是testController,这个是处理过后的 bean 名称,会把 bean 的类名按照驼峰命名处理,所以不用怀疑名称不一致的问题。
Spring 初始化阶段
继续步入到 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons。
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
...
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof SmartFactoryBean<?> smartFactoryBean && smartFactoryBean.isEagerInit()) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
...
}
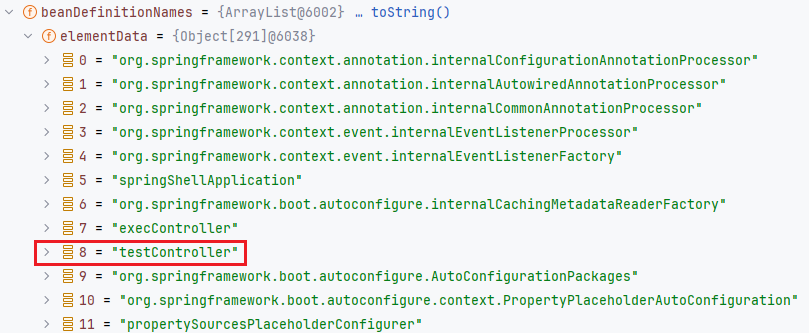
preInstantiateSingletons 方法确保所有非惰性初始化单例都已实例化。先从 this.beanDefinitionNames 获取到所有要实例化的 bean的名称。这里查询的是至少有 290 个,当然也可以看到我们的 TestController 也在里面。也就是说,包含之前注册的 bean 都在这里使用 getBean 实例化完毕了。
通过循环处理所有的 bean,isFactoryBean(beanName) 通过 beanName 判断 bean 是否是 FactoryBean,我们的 Controller 不是接着进入 else 分支,直接执行 getBean 方法。通过执行 getBean 方法返回实例。
步入到 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean。
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
...
}
});
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
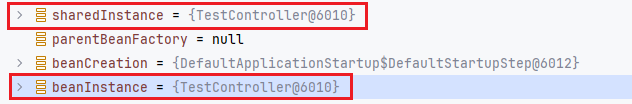
一系列处理和判断之后,判断我们的 Controller 是单例,使用 getSingleton 方法来获取到 sharedInstance。接着使用 getObjectForBeanInstance 方法来得到 beanInstance 对象。
这里我们还看到了 getSingleton 方法的第二个参数是一个 Lambda 表达式,实际返回的值的 createBean(beanName, mbd, args)。这里实际上 getSingleton 方法执行完,sharedInstance 就是等于 createBean(beanName, mbd, args)的返回值。sharedInstance 这个时候只是一个 TestController 对象而已,里面空空的。(???为什么,应该会填充东西进去的啊???)
接着我们步入到 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#getObjectForBeanInstance,最后还是返回了这个对象,也就是说 sharedInstance 和 beanInstance 是一样的。
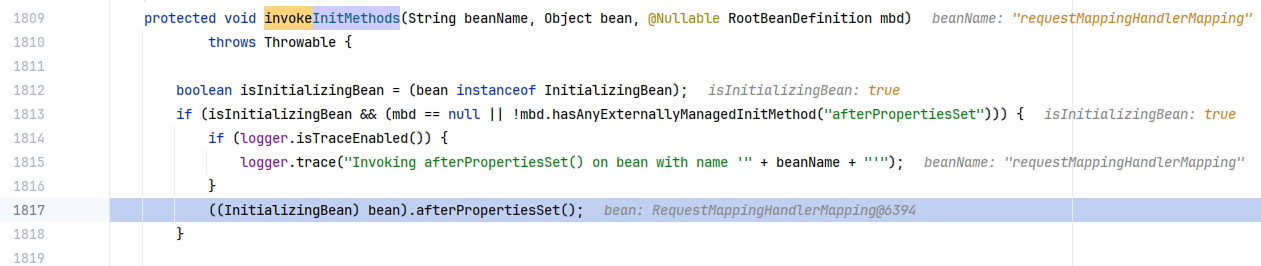
一直到 beanName 是 requestMappingHandlerMapping 的时候,代码继续停在这里一直进入到 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#invokeInitMethods。
Handler 什么?
处理器对象(Handler Object): 这是实际处理请求的组件,通常是一个控制器(Controller)类中的方法,也就是处理器方法。在请求映射阶段,
HandlerMapping会根据请求找到对应的处理器对象。下文中的 Handler 都一般指 Controller。
我们可以看到这里的 beanName 是 requestMappingHandlerMapping 的时候,isInitializingBean 为 true,由于我们 Controller 没有实现 afterPropertiesSet 方法。而 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 这个 bean 是实现了 afterPropertiesSet 方法的。
afterPropertiesSet 方法是什么?
在初始化时检测处理程序方法。如果一个类实现了
InitializingBean接口,Spring 容器在创建该类的实例并完成属性注入后,会调用afterPropertiesSet方法。这个方法提供了一个钩子,让开发者有机会在 Bean 初始化的最后一步执行一些特定的操作,比如初始化数据库连接、加载配置等。
也就是说 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 是有初始化后的默认操作的,第一个操作就是 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#afterPropertiesSet
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
继续步入到 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#initHandlerMethods
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
这里会循环获取当前上下文的所有 bean,每一个 bean 都作为参数执行 `processCandidateBean 方法。
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) { // 在这里判断是否有 Controller 注解
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
在 isHandler(beanType) 判断 bean 是否有 Controller 注解,假如有的话,那么执行 isHandler 方法。我们步入到 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping#isHandler 查看就可以知道。
@Override
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class);
}
接着我们进入 detectHandlerMethods 方法,在这个方法处理 mapping 的映射。也就是路由和方法的映射。
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String beanName ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
...
}
else if (mappingsLogger.isDebugEnabled()) {
...
}
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);// 拿到 Method
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping); // 处理 Method 和路由的映射
});
}
}
这里又是一个 Lambda 表达式,比较复杂,我们拆解分析一下这里。将 methods 的键值对 method, mapping 作为参数循环执行表达式里面的两个 Java 语句。
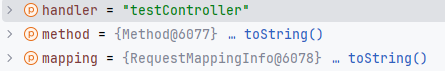
这里两个语句,分别是拿到对应的 Method 对象(实际上就是原来的 Method 对象)和 mapping 映射起来,在这里注册处理映射方法。关键方法是 registerHandlerMethod ,我们内存马的关键代码也就是这个。要三个参数,当前类型分别如下。
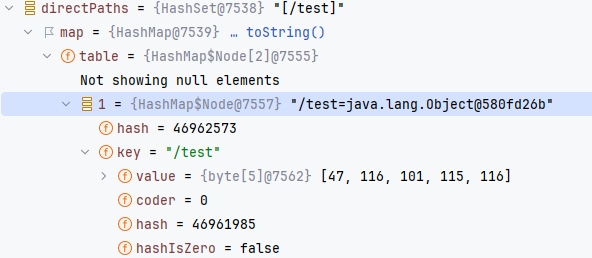
注册实际上是在 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistry#register,具体的逻辑就不分析了,处理映射的语句应该是这句,记录一下当前的参数的内容。
this.registry.put(mapping,new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directPaths, name, corsConfig != null));
mapping 是原来的参数的 mapping,corsConfig != null 是 false。
访问 Controller 调用链
Test:17, TestController (com.example.springshell)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (jdk.internal.reflect)
invoke:77, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (jdk.internal.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (jdk.internal.reflect)
invoke:568, Method (java.lang.reflect)
doInvoke:205, InvocableHandlerMethod (org.springframework.web.method.support)
invokeForRequest:150, InvocableHandlerMethod (org.springframework.web.method.support)
invokeAndHandle:118, ServletInvocableHandlerMethod (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation)
invokeHandlerMethod:884, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation)
handleInternal:797, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation)
handle:87, AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method)
doDispatch:1081, DispatcherServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet)
doService:974, DispatcherServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet)
processRequest:1011, FrameworkServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet)
doGet:903, FrameworkServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet)
service:564, HttpServlet (jakarta.servlet.http)
service:885, FrameworkServlet (org.springframework.web.servlet)
service:658, HttpServlet (jakarta.servlet.http)
internalDoFilter:205, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)
doFilter:149, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)
doFilter:51, WsFilter (org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server)
internalDoFilter:174, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)
doFilter:149, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)
doFilterInternal:100, RequestContextFilter (org.springframework.web.filter)
doFilter:116, OncePerRequestFilter (org.springframework.web.filter)
internalDoFilter:174, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)
doFilter:149, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)
doFilterInternal:93, FormContentFilter (org.springframework.web.filter)
doFilter:116, OncePerRequestFilter (org.springframework.web.filter)
internalDoFilter:174, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)
doFilter:149, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)
doFilterInternal:109, ServerHttpObservationFilter (org.springframework.web.filter)
doFilter:116, OncePerRequestFilter (org.springframework.web.filter)
internalDoFilter:174, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)
doFilter:149, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)
doFilterInternal:201, CharacterEncodingFilter (org.springframework.web.filter)
doFilter:116, OncePerRequestFilter (org.springframework.web.filter)
internalDoFilter:174, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)
doFilter:149, ApplicationFilterChain (org.apache.catalina.core)
invoke:167, StandardWrapperValve (org.apache.catalina.core)
invoke:90, StandardContextValve (org.apache.catalina.core)
invoke:482, AuthenticatorBase (org.apache.catalina.authenticator)
invoke:115, StandardHostValve (org.apache.catalina.core)
invoke:93, ErrorReportValve (org.apache.catalina.valves)
invoke:74, StandardEngineValve (org.apache.catalina.core)
service:340, CoyoteAdapter (org.apache.catalina.connector)
service:391, Http11Processor (org.apache.coyote.http11)
process:63, AbstractProcessorLight (org.apache.coyote)
process:896, AbstractProtocol$ConnectionHandler (org.apache.coyote)
doRun:1744, NioEndpoint$SocketProcessor (org.apache.tomcat.util.net)
run:52, SocketProcessorBase (org.apache.tomcat.util.net)
runWorker:1191, ThreadPoolExecutor (org.apache.tomcat.util.threads)
run:659, ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker (org.apache.tomcat.util.threads)
run:61, TaskThread$WrappingRunnable (org.apache.tomcat.util.threads)
run:833, Thread (java.lang)
Spring 启动完成后的访问 Controller 阶段
在 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#doDispatch
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);
if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new ServletException("Handler dispatch failed: " + err, err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new ServletException("Handler processing failed: " + err, err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
通过 getHandler(processedRequest) 拿到 mappedHandler 对象,我们步入 getHandler 方法看看。
步入到 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#getHandler
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
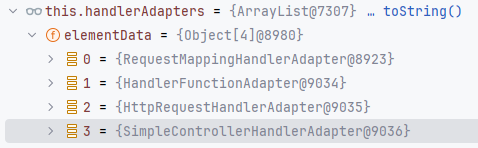
以 HttpServletRequest 对象作为参数,先从 DispatcherServlet 对象中的 handlerMappings 循环获取 handler。我们可以从下图中看到 this.handlerMappings 的内容,有不同的 Mapping 对象,一共有九个。(猜测这里都可以用来注册内存马的映射,后续尝试一下)
显而易见的,这里会循环到 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 才可以获取到 handler。我们步入到 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerInternal 继续查看。
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request); // step into
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
先拿到 lookupPath,这里是 /test,在 lookupHandlerMethod 方法获取 handlerMethod 对象,也就是处理这个路由的方法 Test 了。这里不深入映射获取的细节,具体涉及代码在 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#lookupHandlerMethod。
我们回到 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping#getHandler,getHandler 方法最终就是要返回一个 HandlerExecutionChain 对象。
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
...
return executionChain;
Handler Execution Chain 是什么?
处理器执行链就是将处理器对象和处理器拦截器组合在一起形成的链式结构。这个链条代表了在请求处理的整个生命周期中,请求会经过哪些组件,以及这些组件在处理过程中的执行顺序。
返回到 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#getHandler,我们可以知道这里返回的是一个 HandlerExecutionChain 对象,而不是单纯的 Controller,当然,肯定是包含我们的 Controller 对象的。
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
返回到 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#doDispatch,我把关键的代码提取出来。
// Determine handler for the current request.
// 确定当前请求的处理程序。
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
// 确定当前请求的处理程序适配器。
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // step into
// Actually invoke the handler.
// 实际调用处理程序。
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); // 最终调用反射
HandlerAdapter 会从里面选择其中一个,这里选用的是 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter。在 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter#supports 判断使用哪一个。
只要 handler instanceof HandlerMethod handlerMethod = true ,默认就会选择 this.handlerAdapters 里面的第一个,也就是 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter。
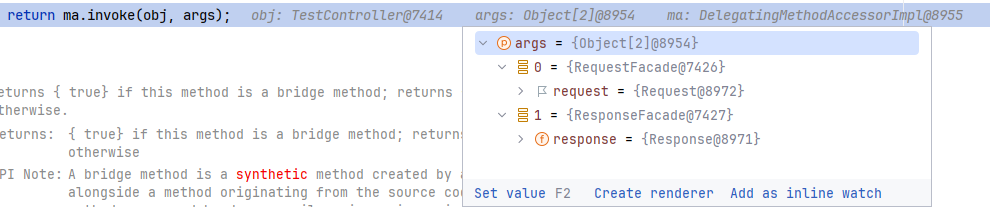
接着,在 handle 方法最终在 org.springframework.web.method.support.InvocableHandlerMethod#invokeForRequest 里面的 return 反射调用处理映射的方法 Test,传入的参数也是 Test 的参数。
至此,基本上完成了从 Spring 启动初始化 和 访问 的两个阶段的关于 Controller 的解析了。
小结
目前看到,注册 Webshell 的最关键代码在于:
org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#detectHandlerMethods
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
接下来,我们需要看看如何使用代码构造需要的参数对象。